- Page 1
- Page 2
- Page 3
- Page 4
- Page 5
- Page 6
- Page 7
- Page 8
- Page 9
- Page 10
- Page 11
- Page 12
- Page 13
- Page 14
- Page 15
- Page 16
- Page 17
- Page 18
- Page 19
- Page 20
- Page 21
- Page 22
- Page 23
- Page 24
- Page 25
- Page 26
- Page 27
- Page 28
- Page 29
- Page 30
- Page 31
- Page 32
- Page 33
- Page 34
- Page 35
- Page 36
- Page 37
- Page 38
- Page 39
- Page 40
- Page 41
- Page 42
- Page 43
- Page 44
- Page 45
- Page 46
- Page 47
- Page 48
- Page 49
- Page 50
- Page 51
- Page 52
- Page 53
- Page 54
- Page 55
- Page 56
- Page 57
- Page 58
- Page 59
- Page 60
- Page 61
- Page 62
- Page 63
- Page 64
- Page 65
- Page 66
- Page 67
- Page 68
- Page 69
- Page 70
- Page 71
- Page 72
- Page 73
- Page 74
- Page 75
- Page 76
- Page 77
- Page 78
- Page 79
- Page 80
- Page 81
- Page 82
- Page 83
- Page 84
- Page 85
- Page 86
- Page 87
- Page 88
- Page 89
- Page 90
- Page 91
- Page 92
- Page 93
- Page 94
- Page 95
- Page 96
- Page 97
- Page 98
- Page 99
- Page 100
- Flash version
© UniFlip.com
- Page 2
- Page 3
- Page 4
- Page 5
- Page 6
- Page 7
- Page 8
- Page 9
- Page 10
- Page 11
- Page 12
- Page 13
- Page 14
- Page 15
- Page 16
- Page 17
- Page 18
- Page 19
- Page 20
- Page 21
- Page 22
- Page 23
- Page 24
- Page 25
- Page 26
- Page 27
- Page 28
- Page 29
- Page 30
- Page 31
- Page 32
- Page 33
- Page 34
- Page 35
- Page 36
- Page 37
- Page 38
- Page 39
- Page 40
- Page 41
- Page 42
- Page 43
- Page 44
- Page 45
- Page 46
- Page 47
- Page 48
- Page 49
- Page 50
- Page 51
- Page 52
- Page 53
- Page 54
- Page 55
- Page 56
- Page 57
- Page 58
- Page 59
- Page 60
- Page 61
- Page 62
- Page 63
- Page 64
- Page 65
- Page 66
- Page 67
- Page 68
- Page 69
- Page 70
- Page 71
- Page 72
- Page 73
- Page 74
- Page 75
- Page 76
- Page 77
- Page 78
- Page 79
- Page 80
- Page 81
- Page 82
- Page 83
- Page 84
- Page 85
- Page 86
- Page 87
- Page 88
- Page 89
- Page 90
- Page 91
- Page 92
- Page 93
- Page 94
- Page 95
- Page 96
- Page 97
- Page 98
- Page 99
- Page 100
- Flash version
© UniFlip.com
Operant Conditioning
Ordering Information
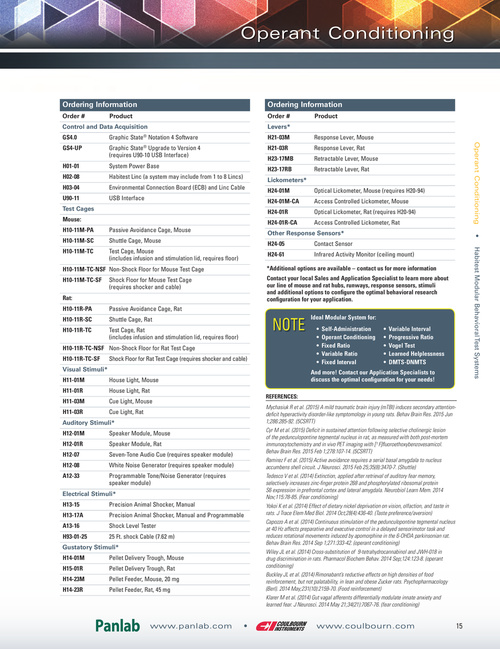
Order # Gs4.0 Gs4-UP H01-01 H02-08 H03-04 U90-11 Test Cages Mouse: H10-11M-PA H10-11M-sc H10-11M-Tc Passive avoidance cage, mouse Shuttle cage, mouse test cage, mouse (includes infusion and stimulation lid, requires floor) Shock floor for mouse test cage (requires shocker and cable) Passive avoidance cage, rat Shuttle cage, rat test cage, rat (includes infusion and stimulation lid, requires floor) Shock floor for rat test cage (requires shocker and cable) House Light, mouse House Light, rat cue Light, mouse cue Light, rat Speaker module, mouse Speaker module, rat Seven-tone audio cue (requires speaker module) white noise generator (requires speaker module) Programmable tone/noise generator (requires speaker module) Precision animal Shocker, manual Precision animal Shocker, manual and Programmable Shock Level tester 25 ft. shock cable (7.62 m) Pellet Delivery trough, mouse Pellet Delivery trough, rat Pellet feeder, mouse, 20 mg Pellet feeder, rat, 45 mg Product graphic State® notation 4 Software graphic State® upgrade to Version 4 (requires u90-10 uSb interface) System Power base Habitest Linc (a system may include from 1 to 8 Lincs) environmental connection board (ecb) and Linc cable uSb interface Control and Data Acquisition
Ordering Information
Order # Levers* H21-03M H21-03R H23-17MB H23-17RB Lickometers* H24-01M H24-01M-cA H24-01R H24-01R-cA H24-05 H24-61 optical Lickometer, mouse (requires H20-94) access controlled Lickometer, mouse optical Lickometer, rat (requires H20-94) access controlled Lickometer, rat contact Sensor infrared activity monitor (ceiling mount) response Lever, mouse Product
Operant Conditioning
response Lever, rat retractable Lever, mouse retractable Lever, rat
Other Response Sensors*
• Habitest Modular Behavioral Test Systems
H10-11M-Tc-nsf non-Shock floor for mouse test cage H10-11M-Tc-sf Rat: H10-11R-PA H10-11R-sc H10-11R-Tc
*Additional options are available – contact us for more information contact your local sales and Application specialist to learn more about our line of mouse and rat hubs, runways, response sensors, stimuli and additional options to configure the optimal behavioral research configuration for your application.
note
Ideal Modular system for: • Self-Administration • Operant Conditioning • Fixed Ratio • Variable Ratio • Fixed Interval • Variable Interval • Progressive Ratio • Vogel Test • Learned Helplessness • DMTS-DNMTS
H10-11R-Tc-nsf non-Shock floor for rat test cage H10-11R-Tc-sf Visual Stimuli* H11-01M H11-01R H11-03M H11-03R H12-01M H12-01R H12-07 H12-08 A12-33
And more! contact our Application specialists to discuss the optimal configuration for your needs!
RefeRences: Mychasiuk R et al. (2015) A mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) induces secondary attentiondeficit hyperactivity disorder-like symptomology in young rats. Behav Brain Res. 2015 Jun 1;286:285-92. (5CSRTT) Cyr M et al. (2015) Deficit in sustained attention following selective cholinergic lesion of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in rat, as measured with both post-mortem immunocytochemistry and in vivo PET imaging with [¹⁸F]fluoroethoxybenzovesamicol. Behav Brain Res. 2015 Feb 1;278:107-14. (5CSRTT) Ramirez F et al. (2015) Active avoidance requires a serial basal amygdala to nucleus accumbens shell circuit. J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 25;35(8):3470-7. (Shuttle) Tedesco V et al. (2014) Extinction, applied after retrieval of auditory fear memory, selectively increases zinc-finger protein 268 and phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 expression in prefrontal cortex and lateral amygdala. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Nov;115:78-85. (Fear conditioning) Yokoi K et al. (2014) Effect of dietary nickel deprivation on vision, olfaction, and taste in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2014 Oct;28(4):436-40. (Taste preference/aversion) Capozzo A et al. (2014) Continuous stimulation of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus at 40 Hz affects preparative and executive control in a delayed sensorimotor task and reduces rotational movements induced by apomorphine in the 6-OHDA parkinsonian rat. Behav Brain Res. 2014 Sep 1;271:333-42. (operant conditioning) Wiley JL et al. (2014) Cross-substitution of ⁸9-tetrahydrocannabinol and JWH-018 in drug discrimination in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014 Sep;124:123-8. (operant conditioning) Buckley JL et al. (2014) Rimonabant’s reductive effects on high densities of food reinforcement, but not palatability, in lean and obese Zucker rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 May;231(10):2159-70. (Food reinforcement) Klarer M et al. (2014) Gut vagal afferents differentially modulate innate anxiety and learned fear. J Neurosci. 2014 May 21;34(21):7067-76. (fear conditioning)
Auditory Stimuli*
Electrical Stimuli* H13-15 H13-17A A13-16 H93-01-25 H14-01M H15-01R H14-23M H14-23R
Gustatory Stimuli*
www.panlab.com
•
www.coulbourn.com
15